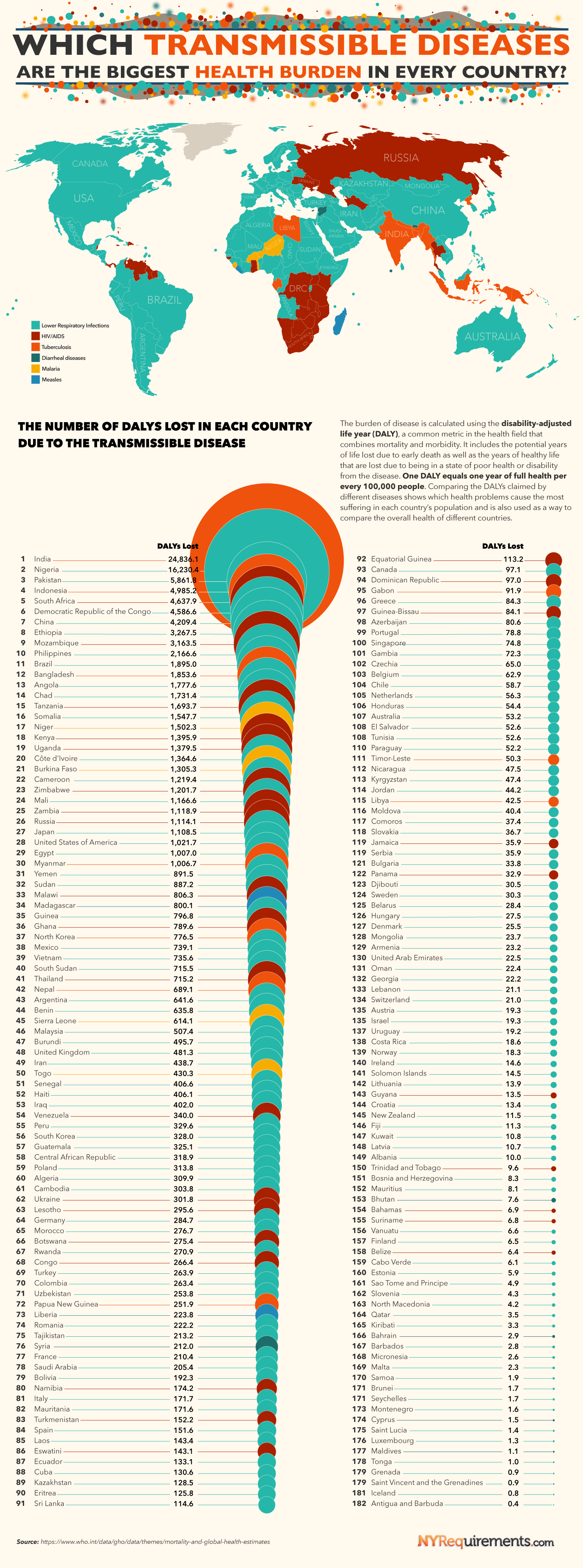
Some transmissible diseases are more of a problem in certain countries than they are in the rest of the world.
The following graphic created by NYRequirements.com displays the transmissible disease that is responsible for the most disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) lost for countries all over the world. These include transmissible diseases like HIV/AIDS, malaria, hepatitis, and measles.
Based on the data from the World Health Organization (WHO), the following is how many countries each of these transmissible diseases are considered the biggest health burdens in:
- Lower Respiratory Infections: 131 countries
- HIV/AIDS: 28 countries
- Tuberculosis: 10 countries
- Diarrheal diseases: 5 countries
- Malaria: 4 countries
- Measles: 2 countries
While measles has been eliminated in many countries throughout the world, it still remains the most dangerous transmissible disease in Madagascar (800.1 life years lost) and Liberia (223.8 life years lost). While measles is a highly contagious disease, the measles vaccine prevented an estimated 23.2 million deaths from 2000-2018, making it one of the most important vaccines available.
Malaria, which is also eliminated in many countries and has been eliminated in the United States since 1951, poses the biggest health burden in Niger (1,502.3 life years lost), Burkina Faso (1,305.3 life years lost), Sierra Leone (614.1 life years lost), and Togo (430.3 life years lost). All four of those countries are located in Africa, where malaria continues to be a very dangerous disease around the continent. It’s estimated by the WHO that there were 627,000 malaria deaths in 2020 and that 93% of global malaria deaths occur in 32 countries in sub-Saharan Africa.

Leave a Reply